Ancient Greece
Learning Objective: What aspects of Greek culture united and divided them?
Subtopics
Subtopics
- Geography
- Government
- Cities
- Religion
- Views and Treatment of Foreigners
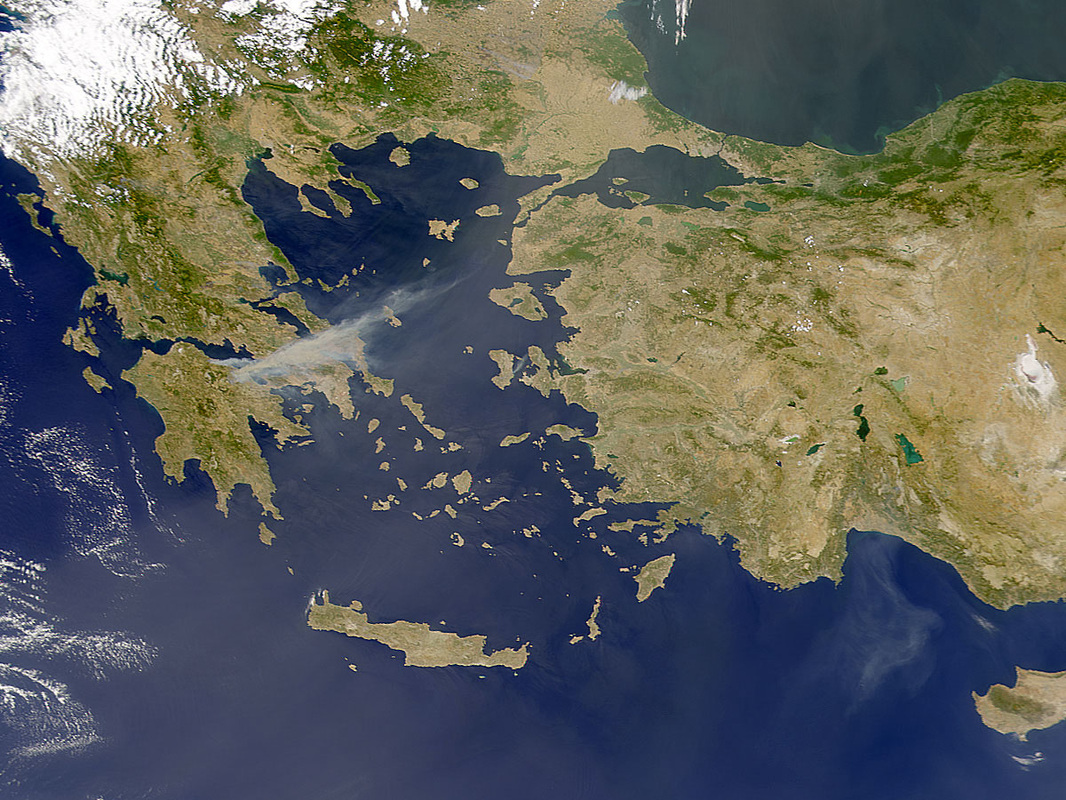
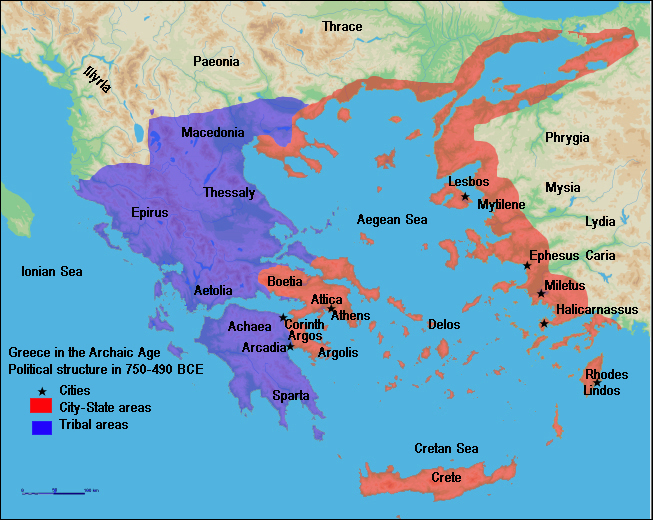
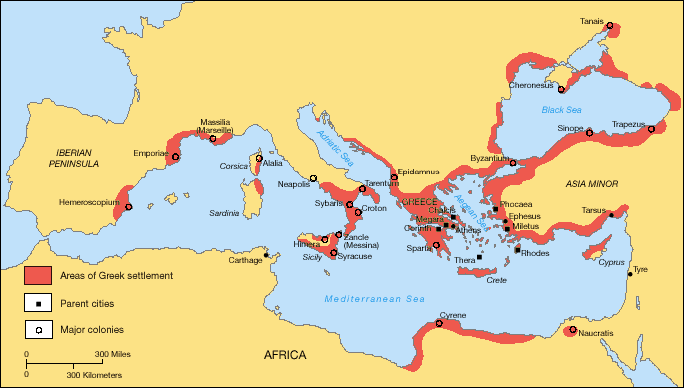
Geography
Ancient Greece Map Exercise
Use the following blank map of Greece [Original Source: http://d-maps.com/pays.php?num_pay=196&lang=en]. It needs to be enlarged to at least half poster size. The final product needs to be colored as a physical map.
Physical Landscape
|
Human Landscape
|
Evaluation
Geography Discussion Questions
- What three ‘continents’ does the Mediterranean Sea unite?
- List the advantages and disadvantages of traveling by sea.
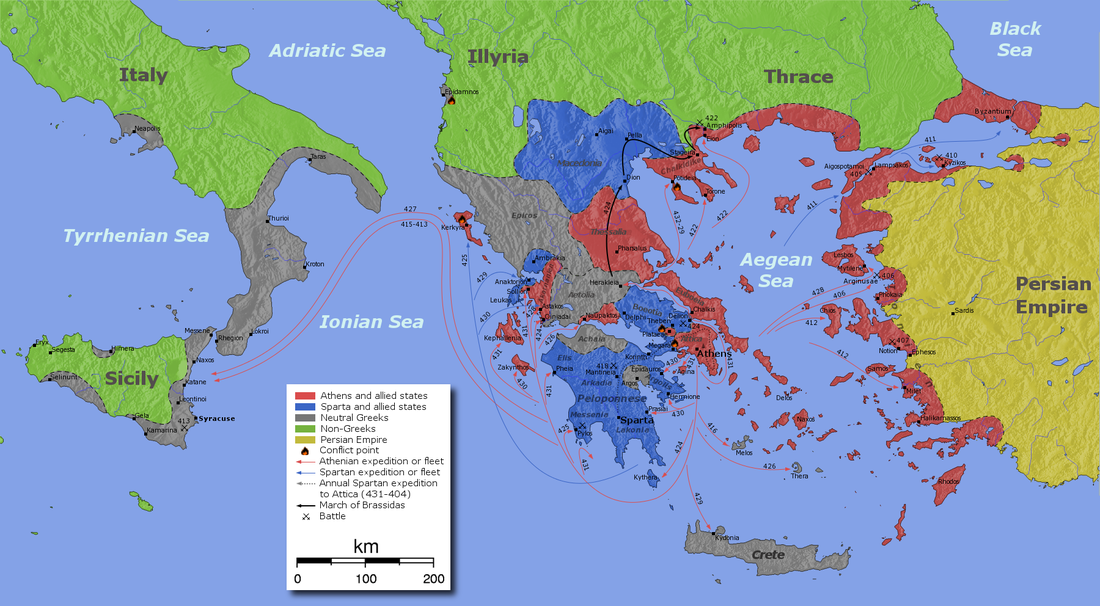
Government
Each polis created its own form of government; however, strong states such as oligarchic Sparta and democratic Athens were able to influence their neighbors. Eventually, these states came into conflict during the Peloponnesian War.
Peloponnesian League led by Sparta
•More Oligarchic
•Agricultural economy •Land-based •Besieged Delian cities by land |
Delian League led by Athens
•More Democratic
•Trade-based economy •Sea-based •Blockaded Peloponnesian ports by sea |
Image Source: Peloponnesian War
Cities: Greek Poleis
Discussion Questions
- What is a Greek Polis?
- What are its main features?
- How and why did it develop?
- What factors caused it to develop the way it did?
- How and why did it spread?
To the Greeks, the Polis was the heart of social and cultural life. Occasionally, Greeks were united by feelings of Panhellenism (being sons and daughters of Helen of Troy), but for the most part, their loyalties were to their individual cities.
Below are pictures of the many of the common elements of a polis. After researching about each element, write a two sentence caption for each picture explaining how these elements united the citizens living in the city.
-OR-
Create a 1-page journal entry (Diary)–of your day in a polis. Visit all of the main places, and tell what you would be doing in each section: acropolis, Agora, Theater, Gymnasium, Bath House, Harbor/Port, House (Underline these terms).
Below are pictures of the many of the common elements of a polis. After researching about each element, write a two sentence caption for each picture explaining how these elements united the citizens living in the city.
-OR-
Create a 1-page journal entry (Diary)–of your day in a polis. Visit all of the main places, and tell what you would be doing in each section: acropolis, Agora, Theater, Gymnasium, Bath House, Harbor/Port, House (Underline these terms).
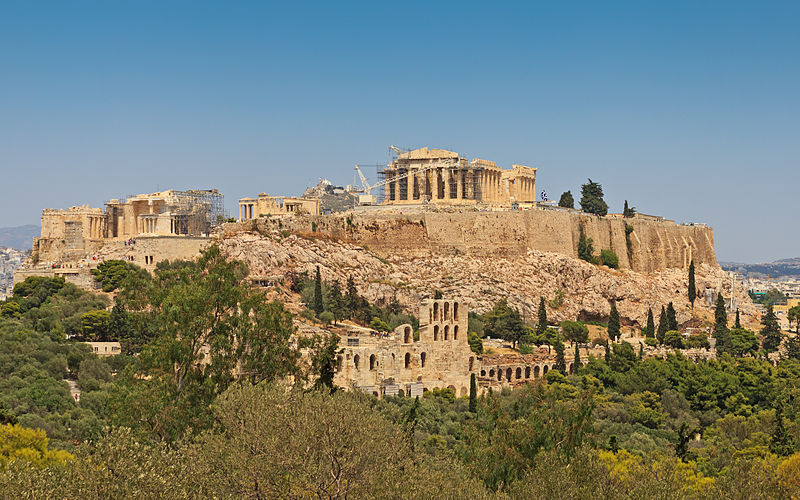
AcropolisAcropolis of Athens. Image source: Wikipeida
|
GymnasiumTechnically, this images is Roman (from Pompeii), but this type of facility would have been common in a Greek polis.
Image Source: Wikipedia |
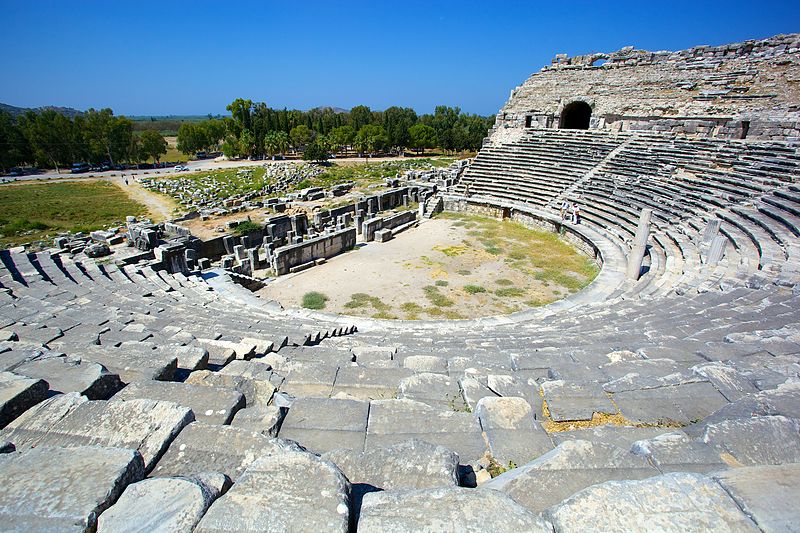
Theater |
Greeks: The Crucible of Civilization, part I
Greek Religion
The Greeks believed in a Pantheon of war-like gods and goddesses that lived on Mount Olympus.
Like Frogs Around a Pond: The Role of Maritime Religion in Ancient Greek Culture and Identity
Like Frogs Around a Pond: The Role of Maritime Religion in Ancient Greek Culture and Identity
Greek Views and Treatment of Foreigners
Greeks had a high level of distrust of anyone that did not come from their polis. However, in times of stress, the Greeks would unite based on sense of shared Greek cultural identity (language, religion, literature, etc.). The Greeks develop strong negative views of non-Greek speakers. They made fun of the sounds they would make by repeating 'bar. . . bar. . . bar' and eventually this became the source of the work barbarian.
Naturally, this hostility was extended towards the Persians, and an a clash between these neighbors became inevitable.
Naturally, this hostility was extended towards the Persians, and an a clash between these neighbors became inevitable.